Wednesday, April 4, 2007
This is from the UN site, a special session on AIDS.
This is the link to the actual site:
click hereGender and HIV/AIDS
Fact Sheet
Global crisis - Global
action
Gender roles and relations powerfully influence the
course
and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. Gender-related factors shape the
extent to
which men, women, boys and girls are vulnerable to HIV infection,
the ways in
which AIDS affects them, and the kinds of responses that are
feasible in
different communities and
societies.
n
Gender inequalities are a major driving force behind the AIDS epidemic. The
different attributes and roles that societies assign to males and females
profoundly affect their ability to protect themselves against HIV/AIDS and
cope
with its impact. Reversing the spread of HIV therefore demands that
women’s
rights are realized and that women are empowered in all spheres of
life.
n Gender-based
inequalities
overlap with other social, cultural, economic and political
inequalities—and
affect women and men of all
ages.
n
A variety of factors
increase the vulnerability of women and girls to HIV. They
include social
norms that deny women sexual health knowledge and practices that
prevent
them from controlling their bodies or deciding the terms on which they
have
sex. Compounding women’s vulnerability is their limited access to economic
opportunities and autonomy, and the multiple household and community roles
they
are saddled with.
n
Men, and
especially young boys, are vulnerable too. Social norms reinforce
their lack of
understanding of sexual health issues and at the same time
celebrate
promiscuity. This vulnerability is further increased by the
likelihood of
engaging in substance abuse (such as alcohol and other drugs)
and of opting for
types of work that can entail mobility and family
disruption (such as migrant
labour or the military).
The impact on women
n In most societies, girls and
women face heavier risks of HIV infection than men because their diminished
economic and social status compromises their ability to choose safer and
healthier life strategies.
n
The
proportion of women living with HIV/AIDS has risen steadily in recent
years. In
1997, 41% of HIV-positive adults were women. Three years later,
that figure had
risen to 47%. In sub-Saharan Africa alone, an estimated 12.2
million women carry
the virus, compared to 10.1 million men.
n Women are often infected at an
earlier age than men. For example, in 1998 most HIV-positive women in
Namibia
were in their 20s, while most men carrying the virus were in their
30s. In some
of the hardest hit countries, girls are five to six times more
likely to be
infected than teenage
boys.
n There
is growing
evidence that a large share of new cases of HIV infection is due to
gender-based violence in homes, schools, the work place and other social
spheres. In addition, in settings of civil disorder and war women and girls
are
often systematically targeted for abuse (including sexual abuse). This
dramatically increases their odds of acquiring HIV and other sexually
transmitted infections, and of experiencing unwanted
pregnancies.
n Research has
shown
that in up to 80% of cases where women in long-term stable
relationships are
HIV-positive, they acquired the virus from their partners
(who had become
infected through their sexual activities outside the
relationship or through
drug
use).
n Women also find
themselves discriminated against when trying to access care and support when
they are HIV-positive. In many countries, men are more likely than women to
be
admitted to health facilities. Family resources are more likely to be
devoted to
buying medication and arranging care for ill males than
females.
n All the while, the
burden of caring for ill family members is made to rest mainly with women
and
girls. As the impact of the AIDS epidemic grows, girls tend to drop out
of
school in order to cope with the tasks of caring for siblings and ill
parents.
Coming to grips with the
challenges
n Experience shows
that
controlling the epidemic depends in large measure on communities’ and
families’
abilities to confront the gender-driven behaviour that increases
the chances of
infection for girls and boys, men and women. That, in turn,
calls for strong and
coherent national policies, strategies and plans.
n The Convention on the
Elimination of Discrimination Against Women (CEDAW) is a key basis for legal
reforms and other steps aimed at countering the violation of women’s human
rights and protecting women who are infected and affected by HIV/AIDS.
n Comprehensive prevention and
care programmes that take into account a wide range of social, economic,
cultural, and political factors are more likely to stem the epidemic. Such
programmes should be marked by high-level political commitment for steps
that
tackle the gender dimension of the epidemic in a variety of ways
(including
legal reforms, as provided in CEDAW, and national HIV/AIDS
policies, plans and
strategies).
n Such programmes
would also
ensure that health information, care and other services are improved
and
provided in ways that are culturally appropriate and gender-sensitive. As
important is the development of sex-specific, gender-balanced information
about
HIV/AIDS and other sexually transmitted infections for different
audiences in
different settings (for example, for young people in and
outside school, or for
workers at home or in the
workplace).
n Innovative
activities
targeting boys and girls are needed to promote more equitable and
mutually
respectful attitudes and behaviour, especially in sexual
relationships. Also
needed are targeted anti-poverty programmes that extend
credit and other forms
of support to both women and men in need, as well as
measures that address the
special needs of widows and children-headed
households.
Thank You!
AAA!
Here is the link to a Powerpoint presentation done by a faculty member of the Department of Family and Social Medicine of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine.
Click HereWe hope that you will enjoy their powerpoint and learn more about HIV/AIDS!
AAA!
Hello!
The Website of the Week is :
Avert.OrgThe link leads to a cool article on the website, check it out!
AAA!
Case History—A Cure?
The following case history was the spark that ignited this in-depth investigation of the causes and pathogenesis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). A 60 year-old-white male, HIV-negative, developed Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) following treatment with a two month course of prednisone (60 mg per day) and a two week course of azathioprine (50-100 mg per day) for lung fibrosis. His blood CD4+ T cells count was 255/µL, the CD4+ T cells /CD8+ T cells ratio was 0.6, and he had severe lymphocytopenia. He also suffered from pneumonia and severe fungal infection in his mouth and skin. Cessation of the treatment with prednisone and azathioprine lead to the reversal of the damage in his immune system. He fully recovered from pneumonia and the fungal infection after a short course of antibiotics and the use of antifungal lotion. Twenty-two days after the last dose of prednisone, his CD4+ T cells count was back to normal at 657 cells/µL (Al-Bayati, 1999).
Review of the literature of the causes and the pathogenesis of AIDS worldwide revealed that approximately 90% of AIDS cases in the USA and Europe are observed in homosexual men and drug users. The regular uses of alcohol, heroin, cocaine, amphetamines, and alkyl nitrite cause chronic health problems of the nervous system, respiratory system, cardiovascular system, kidneys and other tissues in these individuals. The majority of these health problems are usually diagnosed as idiopathic currently, and treated with high doses of glucocorticoids and/or cytotoxic drugs. In addition, homosexual men are usually heavy user of illicit drugs, alcohol, and rectal glucocorticoids ( Fauci et al., 1998; Al-Bayati, 1999).
The HIV-hypothesis states that HIV causes AIDS by killing the CD4+ T cells directly or indirectly after long incubation times (about 10 years), and the number of these cells will reach very low levels (<300/ml) name="Cure3">
However, the treatment of a patient with prednisone at 60 mg per day for about three months can actually cause AIDS as described above. This treatment and doses often given to patients suffering from lung fibrosis, thrombocytopenia, or other chemically induced chronic illnesses. For example, Fauci et al., 1998 (p. 1463) described the treatment for patient with lung fibrosis as follows: "A trial of oral prednisone is begun at a dose of 1 mg/kg daily and continued for about 8 weeks. Should the disease not respond or be progressive, additional immunosuppression with cyclophosphomide should be considered. The objective is to reduce the white blood cell count to approximately half the normal baseline value, causing a distinct drop in the total lymphocyte count. However, a minimum count of 1000 PMNs/µL should be maintained". At this dose levels, the CD4+T cells count in the peripheral blood of the treated individual is expected to be <300/µL which meets the definition for AIDS set by the US Center For Diseases Control and Prevention (CDC).
Further investigation also revealed an astonishing result: the majority of AIDS patients who participated in the four major Zidovudine (AZT) clinical trials in the US between 1987-1992 were HIV-negative prior to their treatment with AZT. Briefly, a total of 2,349 patients participated in these studies, and at least 77% of them were HIV-negative prior to their treatment with AZT. HIV status of participants upon entrance to these studies are:
a) Fischl et al., 1987: 282 patients participated; HIV was isolated at entry from 160 patients (57 percent of the AZT group and 58 percent of the placebo group);
b) Fischl et al., 1990: 406 AIDS patients were treated with AZT but only 50 percent of these subjects had detectable serum levels of HIV antigen before treatment;
c) Volberding et al., 1990: 1338 subjects participated; only 117 patients (9%) had detectable levels of HIV p24 antigen at baseline; and
d) Hamilton et al., 1992: 321 AIDS patients received AZT but only 63 patients (20%) had detectable level of p24 antigen at base-line.
The reversal of CD4+ T cells depletion in the peripheral blood was reported in HIV+ homosexual men after the termination of their treatment with glucocorticoids. Sharpstone et al., 1996 reported that eight HIV+ males with inflammatory bowel disease who used rectal steroid preparation had a decline in their CD4+ T cells at a rate of 85 cells/µL per year. Four of them underwent coloectomy that eliminated the need for the steroid and their CD4+ T cells increased 4 cells/µL per year. Eight case-matched controls who did not have surgery continued to have a decline of 47 cells/µL per year as the result of the use of rectal steroid.
Furthermore, the reversal of the reduction in CD4+T cell count in HIV+ pregnant women following proper feeding was also reported by Fawzi et al., 1998. Briefly, the influence of diet on T cells counts in peripheral blood in 1,075 HIV-infected pregnant women who had poor nutritional status were studied. The CD4+ T cell counts of the women who received multivitamin increased from 424/µL to 596/µL during six months of proper feeding.
The reversal of damage in the immune system in HIV-positive patients following the cessation of the insulting agents and the existence of large number of HIV-negative AIDS patients as described above, combined with the wide use of immunosuppressive agents in modern medicinal practice to treat a variety of drug induced chronic illnesses gave me the incentive to review the medical literature to evaluate the validity of the HIV-hypothesis and the contribution of the illicit drugs, alcohol, and therapeutic agents, and malnutrition to the pathogenesis of AIDS worldwide.
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Source:
Ourcivilisation.comQuestions to ponder:
1. What can we do to stop the spread of AIDS/HIV?
That's all for now!
AAA!
Question: Is it true that when aid/hiv virus is in contact with air it instantaneously dies? How long does it live in droplets ofwater or semen that is in contact with air? What happens forexample in a scenario where person has aids has a cut on hisfinger where some of his blood is dropped on a particular bookcover. Time passes and the blood stain on the book is dried up.The next person who also coincendently also has a cut on hisfinger and the cut comes in contact with dried up blood stainon the book? What are his chances of him getting Aids/HIV?What are the chances of one getting HIV from a toilet seat thathas been left for sometime and the next person sits onit has the tip opening of his penis touch the toilet seat(that has been stained with semen or water)? Would it bepossible for the virus to go through the lining inside of the penisif contacted between semen on the toilet seat and semen fromthe penis (taking consideration if / if not the semen or waterdroplet on seat have been dried up or not?)
SOURCE:
SOURCE DThe lifespan of the virus is about 20 minutes, maximum, in a drop ofblood that lands on a surface outside the body. Once that droplet dries,the virus is dead. No worries there. The chances of you putting thecut portion of your finger on a blood-smear that is fresh enough to containa sufficient amount of live virus to cause infection is infinitely small.20 minutes also holds for body fluids on a toilet seat; this is from anactual experiment. In order to catch it, you would have to bring *broken*skin into contact with the fluid. The virus doesn't get sucked throughmembranes just like that. It needs to have some way into the blood stream.And remember, once the virus particles are exposed to the air, they beginto die. After 20 minutes, there is effectively no live virus left. And a dried smear, certainly, is not going to pose a very great danger.Here is the bottom line: Don't worry about borrowing books from the library. Don't worry about going to the public restroom. You need only worry if you intend to have unprotected sex with a person who has been exposed to the virus. Minute tears and scrapes often occur in the skinduring various sex acts, and *these* are the routes through which the virusis transmitted.
SOURCE:
SOURCE E(This is actually an email from a guy named Mike who posed the questions to a senior chemist who asked his co worker biologist to answer his question)
AAA!
Stefan Lovgrenfor National Geographic News
June 12, 2003
Scientists now say that the simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes), which is believed to have been transmitted to humans to become HIV-1—the virus that causes AIDS—didn't start its life in chimps.
Instead, it was a product of separate viruses jumping from different monkey species into chimps, where they recombined to form a hybrid virus, according to a new study.--------------------------------------------------------------------Source: National Geographic Questions to ponder:- Did HIV really come from monkeys?
- Are monkeys now something to be afraid of?
- If this passage is true, does that mean that the virus HIV can mutate easily?
That's all for now!
+ <3>
Be Free, Stay Free, Live Life!
AAA!
Hello world!
Today,AAA presents...a homemade comic by our very own Grace Ng!
 Thank you,+ <3>
Thank you,+ <3>
Remember, Be Free, Stay Free, Live Life!
AAA!
Tuesday, April 3, 2007

DID you know..?
the highest death rate is AIDS?
the intensity of AIDS?

where aids has spread?

AAA!
In the United States, HIV infection and AIDS have had a tremendous effect on men who have sex with men (MSM). MSM accounted for 70% of all estimated HIV infections among male adults and adolescents in 2004 (based on data from 35 areas with long-term, confidential name-based HIV reporting*), even though only about 5% to 7% of male adults and adolescents in the United States identify themselves as MSM [1,2]. The number of HIV diagnoses for MSM decreased during the 1980s and 1990s, but recent surveillance data show an increase in HIV diagnoses for this group [3, 4]. This increase points to a continued need for culturally appropriate prevention and education services.
Statistics
HIV/AIDS in 2004
In the 35 areas with long-term, confidential name-based HIV reporting, an estimated 19,575 MSM (18,203 MSM and 1,372 MSM who inject drugs) received a diagnosis of HIV/AIDS, accounting for 70% of all male adults and adolescents and 51% of all people receiving an HIV/AIDS diagnosis that year [1].
The number of HIV/AIDS diagnoses among MSM increased 8% from 2003 through 2004. It is not known whether this increase is due to an increase in the testing of persons with risk factors or due to an increase in cases of HIV infection.
Transmission categories of male adults
and adolescents living with AIDS, 2004

Race/ethnicity of MSM living with HIV/AIDS diagnosed during 2001–2004


AIDS in 2004
An estimated 19,611 MSM (17,691 MSM and 1,920 MSM who inject drugs) received a diagnosis of AIDS, accounting for 63% of all male adults and adolescents and 46% of all people who received a diagnosis of AIDS [1].
An estimated 6,630 MSM (5,450 MSM and 1,180 MSM who inject drugs) with AIDS died, accounting for 57% of all men and 42% of all people with AIDS who died [1].
Since the beginning of the epidemic, an estimated 506,213 MSM (441,380 MSM and 64,833 MSM who inject drugs) had received a diagnosis of AIDS, accounting for 67% of all male adults and adolescents and 54% of all people who received a diagnosis of AIDS [1].
Since the beginning of the epidemic, an estimated 295,520 MSM (256,053 MSM and 39,467 MSM who inject drugs) with AIDS had died, accounting for 67% of all male adults and adolescents and 56% of all people with AIDS who died [1].
At the end of 2004, an estimated 210,693 MSM (185,326 MSM and 25,367 MSM who inject drugs) were living with AIDS, representing 66% of all male adults and adolescents and 51% of all people living with AIDS [1].
SOURCE:SOURCE C
AAA!

A diagram of HIV(human immunodeficiency virus).

A diagram of an immune cell(T-helper white blood cell) infected by HIV.
Diagram A:
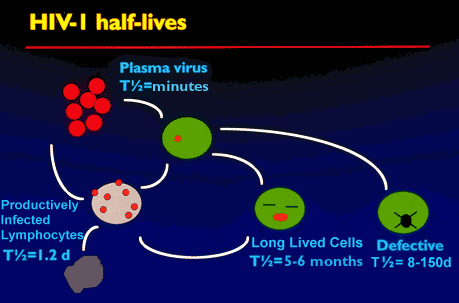
Diagram B:

both diagrams are showing the reproduction of the HIV virus.
AAA!
New reports by UNAIDS and the World Health Organization (WHO) indicate that, as of 2006, the epidemic continues to spread in every region of the world. By now more than 65 million people have been infected with HIV and well over 25 million people have died of AIDS since 1981, 2.9 million in 2006 alone. At this rate, the WHO predicts that in the next 25 years another 117 million people will die, making AIDS the third leading cause of death worldwide.
SOURCE:SOURCE A
Five people worldwide die of AIDS every minute of every day. HIV has hit every corner of the globe, infecting more than 42 million men, women and children, 5 million of them last year alone
Worldwide, and in 2002 alone, AIDS claimed 3 million people last year. That's over 8,000 people every day. But the story does not end there: just under 14,000 new cases of HIV infections occur every single day.
95% of all AIDS cases occur in the world's poorest countries. In several southern African countries, at least one in five adults is HIV positive. In 2000, the HIV prevalence rate among pregnant women in South Africa rose to its highest level ever: 24.5% bringing to 4.7 million the estimated total number of South Africans living with the virus.
That's a terrifying thought. And it's the reality that millions of people in developing countries are living with HIV and AIDS as you read this: communities devastated, teachers and doctors dying every day, people's futures shattered, because they can't afford the drug treatments that are helping people living with HIV and AIDS in richer countries like ours.
Worldwide Statistics
People newly infected with HIV in 2002: 5 million
AIDS deaths in 2002: 3 million...that's over 8,000 deaths per day
Estimated number of people living with HIV/AIDS at the end of 2002: 42 million
Total of AIDS deaths at the end of 2002: 28.1 million
Total number of AIDS orphans: 13.2 million
DO YOU HAVE THE TIME??
SOURCE:SOURCE B
AAA!


SUPPORT SAFE SEX!!! BE FREE, STAY FREE, LIVE LIFE!!!
AAA!
check these out...

how about this??

AAA!
Wednesday, March 28, 2007
WHAT IS AIDS?
AIDS - Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome:
The word Acquired shows that the virus is contagious.
Immune Deficiency - a weakness in the part of the body that fights diseases.
Syndrome - a group of health problems that make up a disease.
AIDS is caused by a virus called HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. If you get infected with HIV, your body will try to fight the infection. It will make "antibodies," special molecules to fight HIV.
A blood test for HIV looks for these antibodies. If you have them in your blood, it means that you have HIV infection. People who have the HIV antibodies are called "HIV-Positive."
Being HIV-positive, or having HIV disease, is not the same as having AIDS. Many people are HIV-positive but don't get sick for many years. As HIV disease continues, it slowly wears down the immune system. Viruses, parasites, fungi and bacteria that usually don't cause any problems can make you very sick if your immune system is damaged. These are called "opportunistic infections."
Source:Source 1
AAA!
Tuesday, March 27, 2007
HELLO WORLD!
WE ARE AAA (BATTERIES)!
Action Against AIDS!
Why do we want to do this?
AIDS is a spreading virus which is very contagious and many are dying from it.The aim of this site is to increase awareness of the disease in society and promote abstinence in unmarried people or at the very least, safe sex.
What will be posted on this site?
1)Info on AIDS
2)Charts & Diagrams
3)A comic strip
4)Detailed illustration
5)An essay/report- written/research report
and other products.
WE HOPE THAT YOU TOO WILL SUPPORT US IN THE BATTLE AGAINST AIDS!
SEE YOU SOON!
AAA
P.S. REMEMBER TO "BE FREE, STAY FREE, LIVE LIFE!"
AAA!